Alsip, Illinois
Alsip, Illinois | |
|---|---|
 Alsip Village Hall | |
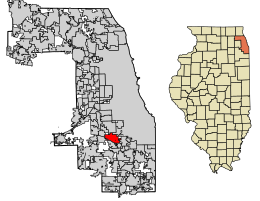 Location of Alsip in Cook County, Illinois. | |
| Coordinates: 41°40′14″N 87°43′56″W / 41.67056°N 87.73222°W | |
| Country | |
| State | Illinois |
| County | Cook |
| Township | Worth |
| Incorporated | 1840 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Mayor | John D. Ryan |
| Area | |
• Total | 6.63 sq mi (17.16 km2) |
| • Land | 6.53 sq mi (16.90 km2) |
| • Water | 0.10 sq mi (0.26 km2) 1.54% |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 19,063 |
| • Density | 2,921.53/sq mi (1,127.97/km2) |
| Standard of living (2007-11) | |
| • Per capita income | $25,286 |
| • Median home value | $202,100 |
| ZIP code(s) | 60803 |
| Area code(s) | 708/464 |
| Geocode | 01010 |
| FIPS code | 17-01010 |
| Website | villageofalsip |
Alsip is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. The population was 19,063 at the 2020 census.[2] It is part of the Chicago metropolitan area.
Alsip was settled in the 1830s by German and Dutch farmers. The village is named after Frank Alsip, the owner of a brickyard that opened there in 1885.[3] The village began to grow after the Tri-State Tollway was built there in 1959.
Geography
[edit]
Alsip is located at 41°40′14″N 87°43′56″W / 41.67056°N 87.73222°W (41.670433, -87.732199).[4]
According to the 2021 census gazetteer files, Alsip has a total area of 6.63 square miles (17.17 km2), of which 6.53 square miles (16.91 km2) (or 98.49%) is land and 0.10 square miles (0.26 km2) (or 1.51%) is water.[5]
Alsip is bordered to the west by the villages of Worth and Palos Heights. To the south is Crestwood. Oak Lawn lies to the north. Merrionette Park, Blue Island, and Robbins lie to the east (north-south, respectively). The Mount Greenwood neighborhood of Chicago lies to the north and east.[6]
Most of the town lies to the north of the Cal-Sag Channel. However, Chippewa Ridge subdivision, which was built upon the former Alsip Nursery, lies southwest of the Cal-Sag. In conjunction with the Illinois Department of Natural Resources and the Water Reclamation District of Chicago, the village operates a boat launch on the canal, permitting inland access to Lake Michigan.[7]
The Alsip area is home to two predominantly African-American cemeteries, Burr Oak and Restvale cemeteries, which are the resting places of many Chicago blues musicians (including Muddy Waters, Willie Dixon and Dinah Washington), athletes (Jimmie Crutchfield), and other celebrities. Emmett Till, whose murder in Mississippi at age 14 in 1955 was an important moment in the Civil Rights Movement, is buried at Burr Oak. In 2004, that cemetery was covered in the national media when the murder investigation was re-opened, and Till's body was exhumed.[8]
Six years later, on July 9, 2010, Cook County Sheriff Tom Dart alleged that four workers at Burr Oak cemetery dug up more than 200 graves, dumped the bodies into unmarked mass graves, and resold the plots to unsuspecting members of the public. The three men and one woman were charged and convicted with one count each of dismembering a human body.[9]
Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 327 | — | |
| 1940 | 541 | 65.4% | |
| 1950 | 1,228 | 127.0% | |
| 1960 | 3,770 | 207.0% | |
| 1970 | 11,608 | 207.9% | |
| 1980 | 17,134 | 47.6% | |
| 1990 | 18,227 | 6.4% | |
| 2000 | 19,725 | 8.2% | |
| 2010 | 19,277 | −2.3% | |
| 2020 | 19,063 | −1.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[10] 2010[11] 2020[12] | |||
As of the 2020 census[13] there were 19,063 people, 7,796 households, and 4,455 families residing in the village. The population density was 2,877.43 inhabitants per square mile (1,110.98/km2). There were 8,016 housing units at an average density of 1,209.96 per square mile (467.17/km2). The racial makeup of the village was 51.58% White, 22.48% African American, 1.95% Asian, 0.70% Native American, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 12.20% from other races, and 11.05% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino residents of any race were 26.52% of the population.
The top five non-African American, non-Hispanic ancestries reported in Alsip as of the 2000 census were Irish (17.1%), German (14.0%), Polish (9.7%), Italian (4.8%) and English (3.5%).
There were 7,796 households, out of which 28.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.60% were married couples living together, 13.94% had a female householder with no husband present, and 42.86% were non-families. 38.13% of all households were made up of individuals, and 20.23% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.27 and the average family size was 2.41.
The village's age distribution consisted of 23.5% under the age of 18, 8.3% from 18 to 24, 26.3% from 25 to 44, 22.7% from 45 to 64, and 19.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39.0 years. For every 100 females, there were 90.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 85.3 males.
The median income for a household in the village was $58,768, and the median income for a family was $72,444. Males had a median income of $48,254 versus $36,313 for females. The per capita income for the village was $30,308. About 7.7% of families and 7.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 4.0% of those under age 18 and 11.3% of those age 65 or over.

| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000[14] | Pop 2010[11] | Pop 2020[12] | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 15,122 | 11,272 | 8,895 | 76.66% | 58.47% | 46.66% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 1,982 | 3,451 | 4,235 | 10.05% | 17.90% | 22.22% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 25 | 18 | 8 | 0.13% | 0.09% | 0.04% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 411 | 434 | 359 | 2.08% | 2.25% | 1.88% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 5 | 5 | 8 | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.04% |
| Other race alone (NH) | 33 | 26 | 50 | 0.17% | 0.13% | 0.26% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) | 420 | 229 | 452 | 2.13% | 1.19% | 2.37% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 1,727 | 3,842 | 5,056 | 8.76% | 19.93% | 26.52% |
| Total | 19,725 | 19,277 | 19,063 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Government
[edit]Most of Alsip is in Illinois's 1st congressional district; the portion north of 115th Street, and the city block northeast of 119th Street and Lawndale Avenue, are in the 3rd district.
Policy-making and legislative authority are vested in the governing Village Board consisting of the Village President, often referred to as the Mayor, and six Trustees, and a Village Clerk. The Village Clerk is an ex officio member of the Board and does not vote. All Board members are elected at large. All Board members serve four-year terms, with the Village President, the Village Clerk, and three Trustees elected usually on the first Tuesday in April following Presidential election year, while the other three Trustees are usually elected on the first Tuesday in April two years later. Beginning with those elected in the April 4, 2017 election, no person may hold the office of Village President, Village Clerk, or Village Trustee for more than three consecutive four-year terms.
The current Village government, as of May 2019 (with the year their term ends):
- Mayor: John D. Ryan (2021)
- Clerk: Susan M. Petzel (2021)
- Trustee: Richard S. Dalzell (2023)
- Trustee: Christine L. McLawhorn (2023)
- Trustee: Christopher W. Murphy (2023)
- Trustee: Michael J. Zielinski (2021)
- Trustee: Monica M. Juarez (2021)
- Trustee: Catalina Nava-Esparza (2021) (Elected to a two-year term to fill the remaining term of Trustee who resigned)
Each trustee and the mayor serve on one or more committees or commissions which oversee government functions. The individual assignments are available at the village website.
There are also a finance director who helps guide the government on fiduciary matters and a law firm that serves as the village attorneys to guide the government on legal matters.[15]
Mayors
[edit]- Gustave Termunde (1927–33)
- Leonard Holmberg (1933–36)
- John Benck (1936–56)
- John J. Alsterda (1956–61)
- Raymond L. Termunde (1961–73)
- Arnold A. Andrews (1973–2005)
- Patrick E. Kitching (2005–2016)
- John D. Ryan (2017–Present)
- Emma Cohen (Future)
Education
[edit]
- Elementary school districts
- Alsip-Hazelgreen-Oaklawn School District 126[16]
- Prairie Junior High School in Alsip
- Atwood Heights School District 125[17]
- Lawn Manor Elementary School in Oak Lawn
- Meadow Lane Intermediate School in Alsip
- Hamlin Junior High School in Alsip
- Cook County School District 130[18]
- Secondary School District
- Community college
- Private schools
- Marist High School, a coed Catholic school in Chicago affiliated with the Marist Brothers
- Brother Rice High School, an all-male Catholic school in Chicago affiliated with the Congregation of Christian Brothers
- Mother McAuley Liberal Arts High School, an all-female Catholic school in Chicago affiliated with the Sisters of Mercy
- Chicago Christian High School
Business and industry
[edit]Alsip is home to the international headquarters of Griffith Laboratories.[21]
One of the two Chicago area Coca-Cola bottling plants is located in Alsip.
Alsip is home to Alsip MiniMill, a producer of corrugating medium using Old Corrugated Containers (OCC) as the primary raw material.
Transportation
[edit]Pace provides bus service on routes 383 and 385 connecting Alsip to destinations across the Southland.[22]
References
[edit]- ^ "2020 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 15, 2022.
- ^ "Alsip village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 23, 2021.
- ^ Callary, Edward (September 29, 2008). Place Names of Illinois. University of Illinois Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-252-09070-7.
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- ^ "Gazetteer Files". Census.gov. Retrieved June 29, 2022.
- ^ "Google Maps". Google Maps. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "Boat Launch". www.alsip.org.il. Archived from the original on May 7, 2008. Retrieved January 17, 2022.
- ^ "Body of '55 civil rights victim returned to grave". Associated Press. June 4, 2005. Retrieved August 24, 2007.
- ^ "Remains from Burr Oak Cemetery scandal reburied - Gary/Chicago Crusader". Chicagocrusader.com. May 19, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- ^ "Decennial Census of Population and Housing by Decades". US Census Bureau.
- ^ a b "P2 Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2010: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – Alsip village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ a b "P2 Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – Alsip village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved June 28, 2022.
- ^ "P004: Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2000: DEC Summary File 1 – Alsip village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "Village Of Alsip". Village Of Alsip. Archived from the original on December 7, 2013. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "District 126 Alsip, Hazelgreen, Oak Lawn ::". Dist126.k12.il.us. Archived from the original on March 3, 2012. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "Hamlin Upper Grade Center - HAMLIN UPPER GRADE CENTER". Ahsd125.org. May 13, 2014. Archived from the original on August 28, 2014. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on October 5, 2015. Retrieved October 4, 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Community High School District 218 - Index". Chsd218.org. June 3, 2014. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "Moraine Valley Community College". Morainevalley.edu. October 4, 2011. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- ^ "Griffith Foods". Griffithfoods.com. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- ^ "RTA System Map" (PDF). Retrieved January 30, 2024.